Art as a Tool for Disseminating Research Outcomes: The Hauā Mana Māori Project and Participatory Action Research in New Zealand
Authors:
Katrina Potiki Bryant, BPhty, PGDipa
Leigh Hale, BSc (Physio), MSc, PhD, FNZCPa
Kelly Tikao, DipNurs, BA, MSciCommb
Stephan Milosavljevic, BAppSc, PGDip (Manips), MMPhty, PhD
Tracey Wright-Tawha, PGDipc
Aimee L. Ward, BS, MPHa
Brigit Mirfin-Veitch, BA, BA (Hons), PhDb
aSchool of Physiotherapy
University of Otago
PO Box 56, Dunedin, 9054, New Zealand
Telephone: +64 3 479 5422
bDonald Beasley Institute
PO Box 6189, Dunedin 9059, New Zealand
Telephone: +64 3 479 5860
cNga Kete Matauranga Pounamu Charitable Trust
92 Spey Street, Level 1 Reception, Invercargill, 9810, New Zealand
Telephone: +64 03 214 5260
Corresponding author:
Professor Leigh Hale, Centre for Health, Activity, and Rehabilitation Research, School of Physiotherapy, University of, Otago, PO Box 56, Dunedin 9054, New Zealand, Email: leigh [dot] hale [at] otago [dot] ac [dot] nz, Telephone: +64 3 4795425
Introduction
Background
The concept of patient-centeredness is a widely accepted approach, but has only recently expanded from the environment of health care delivery to health care research. An important component of this approach is built upon the belief that including participants and end users of research in the research process will enhance recruitment, increase likelihood of actual translation of evidence into practice and more efficiently extend benefits to target patient populations.1 An example of this type of collaborative research project was the Hauā Mana Māori study. Researchers worked alongside hauā (disabled) Māori (tāngata whenua – the indigenous people of New Zealand) in the Southland region of the South Island of New Zealand (NZ). Together they investigated hauā Māori access to health services and to their community by exploring the perceptions of what makes this group feel both enabled and disabled.2
New Zealand is a multicultural society, with Māori comprising the indigenous population. As of the 2013 census, there are 4.43 million people living in NZ;3 14.9% (598,605) of the population identified their ethnicity as Māori.4 The Treaty of Waitangi is considered to be NZ’s founding document, and was signed in 1840 between Māori and the Crown (Great Britain). Of particular relevance for health in Aotearoa (New Zealand), the Treaty specifies that the well-being of Māori be protected alongside all NZ residents. In particular, Article 3 ‘oritetanga’ (equity) guarantees that Māori share equally in the benefits of modern society including equal standards of health care, equality of access to health care, and a general equality of health outcomes.5 Integral to the Treaty are core principals of partnership, participation and protection. Thus the Treaty emphasizes Māori participation in determining all processes for best practice, in both clinical care and in research.5
Disability is a substantial concern for Māori. Approximately 26% of New Zealand’s population identify with having some form of disability that impacts their life.6 The disability rate for Māori was 19% (95,700 people) in 2006.7 About half of Māori living with disability are under the age of 25 years.8 Several factors contribute to this age-related difference, including higher mortality in earlier age groups, lower life expectancy,9 earlier onset of age-related illness and disease,10 and a higher birth rate.11 Mobility disability and agility disability are the most common types of disability experienced by Māori adults.7
To improve access to disability services and support for Māori living with disability and their whānau (extended family), the initial aims of the study were to explore and understand current access. Jones et al suggest that health services in the past have largely failed to acknowledge Treaty obligations, ignoring cultural differences and “assumed that the Pākehā (New Zealanders of European descent) way of doing things is a norm”.12, p1 Recently, the Ministry of Health launched an action plan for disability support services to guide actions to address the needs and priorities of Māori who are disabled.13 The action plan reiterates that if services do not acknowledge the significance of culture in the assessment and support of hauā Māori, there is a greater chance that the outcomes will be poorer health.13
In Māori concepts of health, there is no distinction between health and disability, and thus no clear definition of disability. The concept of “wellness” is better understood, and is perceived to be more linked to an individual’s ability to contribute to their iwi (tribe) and whānau, thus based not on personal performance per se, but performance within a wider community setting.13,14 Therefore, our research viewed both Māori living with disability and their whānau as entwined and not separate entities. Further, as reported by Harwood, it is up to each whānau to define for themselves who their whānau are, thus a broad perspective was taken within our research, and the terms “disability” or “whānau” were not predetermined.15
Ethical approval for our study was obtained from the University of Otago Ethics Committee (Ethics Committee’s reference code: 12/175) and also from the Ngāi Tahu Research Consultation Committee (as the work originated within the tribal area of Ngāi Tahu, the local iwi). This consultation process ensured the research was conducted in a manner that respected Māori ideologies and world-views, would result in quality research of significance to Māori, and had the potential to bring about beneficial change.
The study used a mixed methods approach, based on a case study design. Data were collected from hauā Māori and their whānau, and from organizations providing health and disability services in Murihiku, via face-to-face interviews, group meetings, and group concession. To support the autonomy of individuals with disability, Participatory Action Research (PAR) was used to listen to the voices of the hauā Māori, including respecting their preference for study finding dissemination options.17
Integral to the study was the development of a rōpu kaiārahi (advisory group). This group guided and advised us through the planning, development, outcome delivery stages of our study, and finding dissemination. Additionally, a kaumātua (local elder) was invited to be the group leader on the study, and to help researchers support the study’s kaupapa (proposal) among community groups and health providers. Further description of PAR and the methodology of data collection can be found elsewhere.2
At a hui (meeting) during the development phase of the study, we consulted with the rōpu kaiārahi to gain insight into possible ways for disabled Māori and their whānau to express their voices and share stories about living with a disability. Different approaches were suggested based upon age groups, (for example, individual interviews for older adults, focus groups for middle aged adults, and Facebook or a blog discussion for the younger generation); groups/forums led by the kaumātua; creating some piece of art through kōrero (storytelling), hopu whakāhua (photography), or waiata (song); or the use of multi-media. By utilizing various artistic mediums, the study participants were able to articulate a “picture” of what it is to be Māori living with a disability.
Therefore, the purpose of the current paper is to describe a collaborative effort with study participants to develop a unique method of disseminating research results through an art exhibition. This process illustrates a creative avenue to engage communities in research through a humanities-based platform that provided a broader perspective of an indigenous culture’s experience of disability.
Participants and recruitment
Participants, as well as the Ngā Kete Mātauranga Pounamu Charitable Trust in Murihiku, were consulted about the concept of an art exhibition as a way of disseminating the research findings and the idea was met with excitement and support from all. The Ngā Kete Mātauranga Pounamu Charitable Trust is a Māori health provider in Murihiku. Services offered by the Trust range from connecting Māori and their whānau with community resources, providing mobile nursing services and counselling for various issues, as well as student and employment support. The Trust supported and guided us in the planning of the art exhibition.
For the Hauā Mana Māori study, the recruitment goal was 30 adult Māori (16 years and older) who identified as living with a disability, and also Māori whānau or care givers who identified as living with hauā Māori, residing in Murihiku. These same participants were interviewed about their thoughts on how to disseminate results.
Table 1 displays the characteristics of participants from the Hauā Mana Māori study. Of the 34 Māori living with disability that volunteered for the original study, 29 were interviewed (18 males and 11 females). All participants lived in the surrounding community. Some individuals were unable to continue to participate throughout the entire study, as a result of personal or whānau commitments. Our final rōpu kaiārahi consisted of sixteen people who attended and volunteered to be part of the Hauā Mana Māori study, and these 16 also contributed to the art exhibition.
Table 1: Characteristics of participants in the Hauā Mana Māori study
| Characteristics | Category | n = 29 |
| Age
Range: 17-74 years
|
16 – 19 years
20 – 29 years 30 – 39 years 40 – 49 years 50 – 59 years 60 – 69 years > 70 years |
1
2 2 8 7 7 2 |
| Iwi (Tribe)
(some participants reported multiple iwi) |
Ngāi Tahu
Ngā Puhi Waitaha Tainui Kāti Māmoe Ngāti Kuri; Rakiura; Maniopoto; Ngāti Porou; Ngāti Kahungunu; Te Atiawa |
17
6 3 2 2 1 |
| Disability
(some participants reported multiple disabilities) |
Hearing impairment
Diabetes Arthritis Heart Visual impairment Stroke Multiple Sclerosis Epilepsy Blood clotting problem Chronic pain Sarcoidosis Recovering from cancerous tumour removal Asthma Anxiety Meningitis Dialysis Dyspraxia Fractured femur Alzheimer’s disease Alcohol foetal syndrome Schizophrenia |
4
4 3 3 2 3 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
Procedures
Although art work was a method favored by the rōpu kaiārahi as a way to collect meaningful data, researchers jointly decided with participants that time constraints would limit the ability to hold a hui (meeting) needed to effectively utilize this form of data collection. Instead, the rōpu kaiārahi suggested using a visual method to disseminate the study findings to the broader community. As part of their routine, all participants regularly used art as a way to structure their day, to network into other community groups and ultimately to enhance their hauora (health), wairua (spirit), and mauriora (community voice). Consequently, a two-day art exhibition was planned to distribute study findings to the broader community in Invercargill, Murihiku (Figure 1), honoring the individuals who took part in the study and those other individuals and groups they represented within the disability community.

Figure 1: Discussion of emerging findings with members of the rōpu kaiārachi and Nga Kete Matauranga Pounamu Charitable Trust
In addition to sharing study results, this exhibition would offer a formal way for the rōpu kaiārahi to conclude the Hauā Mana Māori study, an important facet of Māori culture. This ceremonial conclusion by a kaumātua included a karakia whakamūtunga (closing blessing) on the last day, to formally and spiritually close the Hauā Mana Māori study.
Study participants were invited to create an art piece to express themselves; their life, dreams, disability, wellness, challenges and interactions with services and community. The art piece could be in any medium, such as words (poetry/story format), music, paint, clay, cardboard, or stone. Grant funds provided some financial resources to support art supplies as needed.
The main themes that emerged from previous work with respect to our study participants’ perspective of good health were whakamana (being valued), whānaukataka (relationships), a healthy sense of self-identity and self-worth, and good access to resources. Conversely, in terms of disability, the main themes included the negative impacts of discrimination, colonization, and disconnection, as well as lack of self-worth and poor access to resources. These themes were expressed in one way or another during the art exhibit.
Using this option of dissemination at the end of the study served many functions. The opening of the art exhibition provided a means to gather again everyone involved in the research, to present the findings, to obtain constructive feedback from the participants as to whether the researchers were presenting their views correctly, and to allow the participants to relay their feelings of being involved with the study. The event was well received by both participants and the public, and the emotional impact of the art gallery filled with participants, whānau, members of the community, and health care providers was quite powerful and affirming.
Some examples of artwork are provided below (Figures 2, 3 and 4).
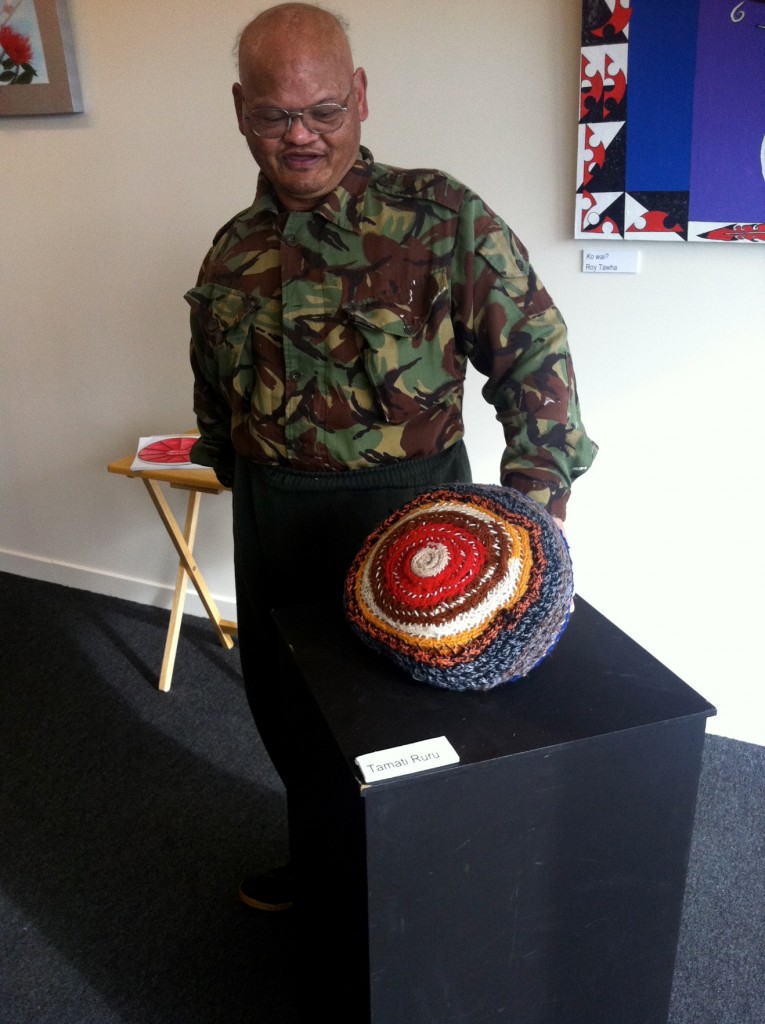

Figure 2: Examples of Art Work
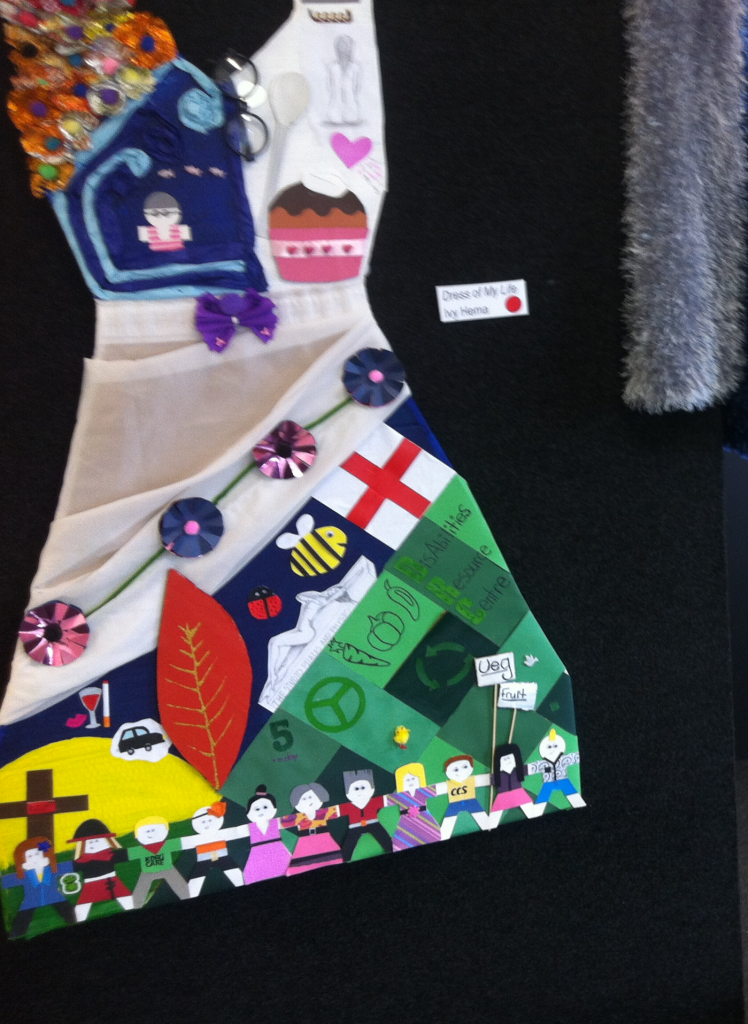

Figure 3: Examples of Art Work
Discussion
Based on the suggestions during the main research phase and through the art exhibition, many strategies were recommended to better facilitate disabled Māori and whānau access of Murihiku health and disability support organisations.
Participants in this research consistently identified that feeling valued as people positively facilitated their access to health and disability services. They offered a wide range of suggestions to improve healthcare provider interactions with clients, including being viewed as an active contributing member of the community, receiving respect and a positive attitude from the community, being listened to, not being discriminated against, being provided with choice, and being provided with a flexible approach.
Feeling connected to each other and the healthcare process was also important to the participants. Consequently, suggestions for community and healthcare organisations included being intentional in facilitating connections with and understanding the importance of whānau, appreciating that friends and community in addition to immediate family are considered whānau, endeavouring to be more “whānau-centred” and “whānau-led”, and facilitating and being responsive to feedback from the disabled community.
Clinicians can foster self-worth in their clients by not assuming, but specifically asking about ethnicity, acknowledging and respecting an individual’s strong belief in a religious faith, offering karakia (ritual chants) if requested, and allowing time and space for rangimarie (peacefulness), facilitating aroha (love) and mana (governing of self). This cultural sensitivity can be fostered by spending time building relationships with their clients, endorsing Māori health models, encouraging a sense of Māori identity, and being accountable to service policies and strategies that incorporate the Treaty of Waitangi.
By incorporating these suggestions into clinical care, organizations can be better advocates for their clients, improve client access, better advertise and market their services to the Māori community and Māori organisations,network with other organisations (especially with Māori health providers), provide appropriate information in a wide range of formats (such as plain language, different languages, audio-recordings) and reinforce this information face-to-face with the client.
The primary recommendation arising from this hauā Māori health and disability services access research was the establishment of an Advocacy Service in Murihiku. Many Māori rely on whānau to awhi (assist) them in times of need. Whānau, however, are not always close or available. Having an advocate to awhi or support hauā Māori access organisations and who are responsive to their needs is critical to improving access to health and disability organisations in Murihiku. This advocate could take on a range of roles, for example, accompanying the hauā Māori to the specialist, assisting them to identify and ask pertinent questions and ensure the hauā Māori is satisfied his or her questions have been answered. On a more practical level, advocates could assist with transport and with accessing other support that hauā Māori may require.
Conclusion
The Hauā Mana Māori study illustrates how research dissemination can be non-conventional and tailored to diverse cultures. More specifically, the study demonstrated how PAR was responsive to disabled Māori, in this case in the Murihiku community. Both hauā Māori and the method of PAR were central to the research from the early planning stages all the way through to the dissemination of findings and promotion of jointly constructed recommendations. This paper specifically described a unique process of dissemination that provided an innovative and essential way for participants in this study to express their realities to their local community through a range of creative forms, from music to bag making, jewelry, knitting, painting, collage and poetry. As one art exhibit participant who displayed his knitting put it, “Being able to express myself in my knitting is so important to me. People can’t believe that I can do this and they love it.”
Feedback from one participant summed it all quite well: “I did not know what to expect from being involved in this study. I came here especially to tell you that following this experience with you, being interviewed and talking with you, I have really looked at what would help me be healthy. I have to thank you because I have a better view of what that is now and I have made some positive changes in my life, and I feel so much better for it.”
Acknowledgements
Nga mihi nui koutou (many, many thanks) to Melanie Reed (Ngā Kete Mātauranga Pounamu Charitable Trust, Murihiku) and the study’s Rōpu Kaiārahi (advisory group) for their guidance and support.
This study was funded jointly by jointly funded by the New Zealand Ministry of Health (MoH) and the Health Research Council of New Zealand (HRC).
References
- Frank L, Basch E, Selby JV. The PCORI perspective on patient-centered outcomes research. JAMA 2014; 312 (15):1513-1514. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.11100.
- Hauā Mana Māori: Living unique and enriched lives. The Centre for Health and Rehabilitation Research. http://www.health.govt.nz/publication/haua-mana-maori-living-unique-and-enriched-lives. Published March, 2014. Accessed March, 2014.
- New Zealand in Profile: 2013. Statistics New Zealand: Wellington. stats.govt.nz. Published December, 2013. Accessed November, 2015.
- Census QuickStats about Maori. Statistics New Zealand: Wellington. stats.govt.nz. Published December, 2013. Accessed November, 2015.
- Waitangi Tribunal. Principals of the Treaty. waitangi-tribunal.govt.nz/treaty/principalsasp. Published Accessed August, 2012.
- Disability Survey. Statistics NZ: Wellington, NZ. Published December, 2013. Accessed November, 2015.
- Disability and Māori in New Zealand in 2006: Results from the New Zealand Disability Survey. Office for Disability Issues and Statistics New Zealand: Wellington. Published 2010. Accessed November, 2015.
- Cunningham C, Durie M, Fergusson D, Fitzgerald E, Hong B, Horwood J, et al. Ngā Āhuatanga Noho o te Hunga Pakeke Māori: Living Standards of Older Māori. Ministry of Social Development: Wellington. msd.govt.nz. Published 2002. Accessed November, 2015.
- Blakely T, Robson B, Tobias M, Bonne M. Decades of disparity: ethnic mortality trends in New Zealand 1980-1999. Ministry of Health and University of Otago: Wellington. http://www.moh.govt.nz. Published July, 2003. Accessed November, 2015.
- Births and birth rates, total and Maori populations 1962-2009. Statistics New Zealand: Wellington. stats.govt.nz. Published 2010. Accessed November, 2015.
- United Nations declaration on the rights of indigenous peoples. United Nations: Geneva. Asia Pacific Forum of National Human Rights Institutions and the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights. Published August, 2013. Accessed November, 2015.
- Jones R, Crengle S, McCreanor T. How Tikaka guides and protects the research process: insights from the Hauora Tane project. Social Policy J NZ 2006; 29(18):60-78.
- Whaia Te Ao Marama: The Maori Disability Action Plan for Disability Support Services 2012 to 2017. Ministry of Health: Wellington. http://www.moh.govt.nz. Published 2012. Accessed November, 2015.
- Living with Disability in New Zealand: A descriptive analysis of results from the 2001 Household Disability Survey and the 2001 Disability Survey of Residential Facilities. Ministry of Health: Wellington. http://www.moh.govt.nz. Published 2004. Accessed November, 2015.
- Harwood M. Rehabilitation and indigenous peoples: the Maori experience. Disabil Rehabil 2010; 32(12): 972-977.
- Gilgun JF. A case for case-studies in social-work research. Social Work 1994;39 (4): 371-380.
- Seekins T, White GW. 2013. Participatory action research designs in applied disability and rehabilitation science: protecting against threats to social validity. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2013;94 (1 Suppl):S20-29.
Appendix
Initial invitation letter to participants
Whaowhia te kete Matāuraka – Fill the basket of life
We were thinking of creative and exciting ways to share with the community the outcomes of the Hauā Mana Māori research project. Whilst pondering this thought we were reminded how clever and arty many of our participants are and perhaps we should look at an exhibition as a way to express the project.
Hence, we are now seeking an art piece in any medium that you have created in the past, recently or would like to create now to express YOU, to express your life, your dreams, your disability, your wellness, your challenges and your interactions with services and your community.
Your piece could be in: words (poetry/story format), music, paint, clay, cardboard, stone….whatever medium you like to work with.
We can provide a small amount of pūtea towards resources you may need to buy in order to create a new piece.
To confirm your involvement in this exhibition you need to contact Kelly or Katrina on the contact details below before the 15th of April 2013.
The exhibition opening date is the 16th of May, 2013*. Venue yet to be confirmed. The opening of the exhibition will also provide a platform to promote the recommendations that have arisen from the project outcomes
You will require your wonderful creation to be completed and delivered to (we can pick up if you are unable to drop it to the venue), venue to be decided, by the 6th May, 2013.
Kelly and Katrina are here to answer any questions and to support you along the creative process. Having you involved in the conclusion of this project is very special.
The exhibition will be open to the public to view over a two week period and we may be looking for volunteers to look after the exhibition whilst it is up. If you would like to be part of this exhibition by creating an art piece or submitting an already completed piece OR by volunteering to help out during the exhibition please connect with us.




 Member since 2019 | JM14274
Member since 2019 | JM14274

NO COMMENT